| SPATA2 |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | SPATA2, PD1, PPP1R145, tamo, spermatogenesis associated 2 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 607662; MGI: 2146885; HomoloGene: 4407; GeneCards: SPATA2; OMA:SPATA2 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 20 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 20q13.13 | Start | 49,903,391 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 49,915,529 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 2 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 2|2 H3 | Start | 167,323,053 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 167,334,807 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
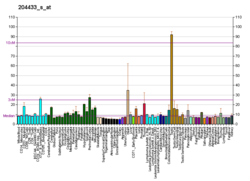
| Top expressed in | - secondary oocyte
- middle temporal gyrus
- endothelial cell
- Brodmann area 23
- primary visual cortex
- right frontal lobe
- prefrontal cortex
- Brodmann area 9
- C1 segment
- caudate nucleus
|
| | Top expressed in | - otic vesicle
- lobe of cerebellum
- zygote
- cerebellar vermis
- dentate gyrus of hippocampal formation granule cell
- subiculum
- visual cortex
- primary motor cortex
- primary visual cortex
- hippocampus proper
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 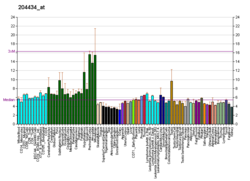
 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- molecular function
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- nucleus
- fibrillar center
| | Biological process | - multicellular organism development
- cell differentiation
- spermatogenesis
- regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway
- regulation of inflammatory response
- regulation of necroptotic process
- protein K63-linked deubiquitination
- protein linear deubiquitination
- programmed cell death
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 20: 49.9 – 49.92 Mb | Chr 2: 167.32 – 167.33 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

















